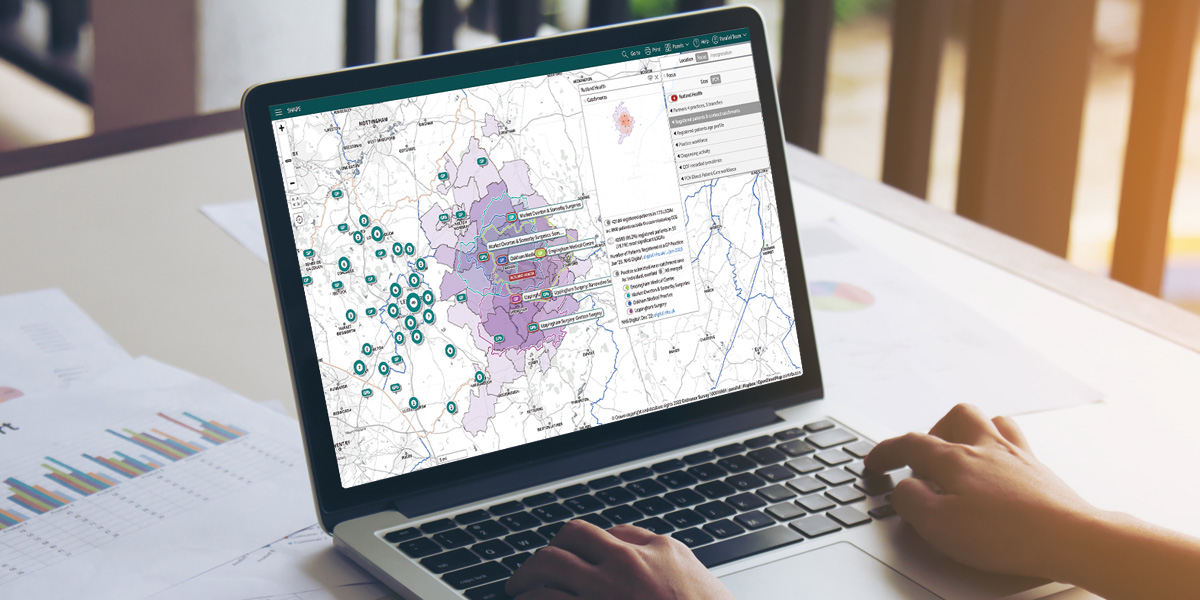
SHAPE maps ideal locations for CDCs
Community Diagnostics Centres (CDCs) are central to the Government’s plan to reduce NHS waiting lists and have already significantly bolstered capacity, delivering an additional three million checks since the initiative started in July 2021.
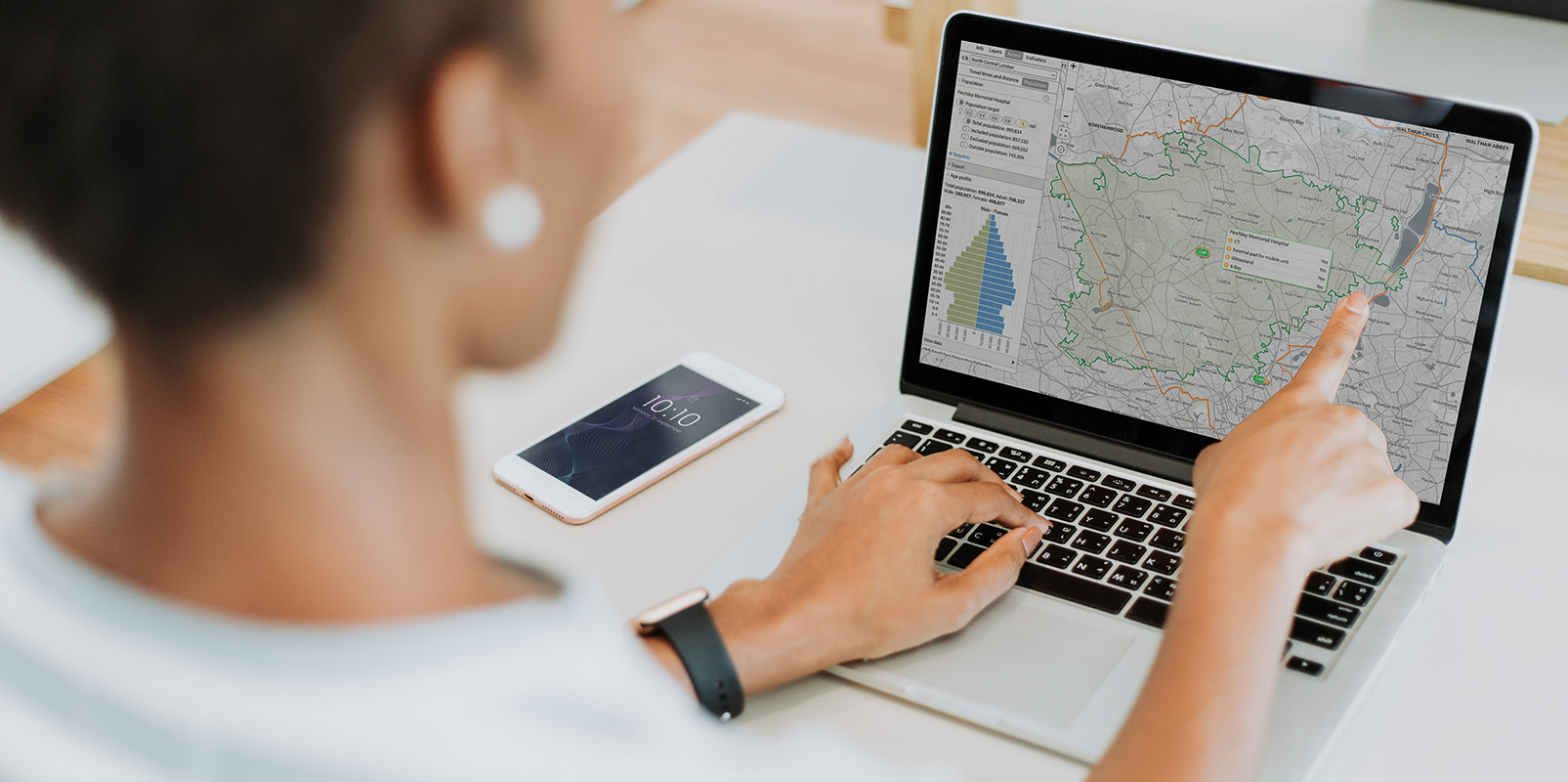
As part of the programme, ICBs across the country are utilising the mapping tool SHAPE to assess the best locations for ‘hub and spoke’ set ups so to that people can quickly and easily access the tests they need, such as MRI, CT, x-ray and ultrasound scanners in their local community.
SHAPE enables ICBs to map demand across a geographic area and overlay information about where mobile testing units can be positioned to meet the greatest levels of demand. The SHAPE team have built capabilities to filter sites based on size of concrete bases and adequate power supply to support the assessment and suitability of different locations.
Issy Whitelock from Shared Agenda who has been leading on this project for several ICBs, said:
“The hub and spoke model for CDCs allows ICBs to have a central hub to deliver key diagnostic testing such as scans, blood tests and blood pressure monitoring, alongside a network of satellite locations in local communities that mobile units or pop ups can be located to provide additional capacity.
“The mapping work through SHAPE provides an insight into where these would be best positioned to meet the needs of local people, supporting the decision making process and enabling ICBs to get services set up quickly.”